General Journal: Definition, Example, Format, and Explanation
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
Description
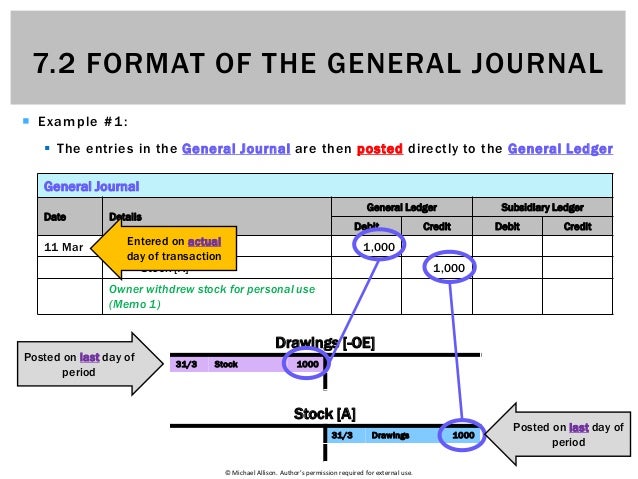
This column is used to record the amounts of the accounts being credited. This column is used to record the amounts of the accounts being debited. There could be more specific journals, but the four accounting areas that these represent contain the bulk of all accounting entries, so there is usually no need for additional journals. And, we will record withdrawals by debiting the withdrawal account – Mr. Gray, Drawings. As you can see in the general journal template above, the key information that should be included at the top is the name of the entity and the period that the journal is recording. If financial statements are not put together in the correct order, then the information that they contain would be incorrect.
Are General Journals the Same as General Ledgers?
Recording business transactions in the general journal using journal entries is the second step in the accounting cycle of the business. The Accounting Cycle refers to the steps that a company takes to prepare financial statements. The general journal was more visible in the days of manual record keeping. With nearly everyone now using accounting software to record their accounting transactions, it is not so readily apparent. Instead, the software makes it appear as though all transactions center around the general ledger, with no specialty journals in use at all. It’s important to note that more complex transactions might affect more than two accounts.
Journal Entry: Definition
These entries would then be totaled at the end of the period and transferred to the ledger. Today, accounting systems do this automatically with computer systems. A general journal is a chronological record of a company’s financial transactions. These include reconciling accounts and helping to produce financial statements.
Using Accounting Software
Ensuring that you record dates properly will help keep your journal organized and accurate. In the above table of general journal examples, we can see each transaction as two lines- one debit and one credit account. You are likely to make mistakes when using journals, thus, you can easily check for mistakes by adding both sides of your journal entry together. If they do not equal the same number, then there is an error nd you should know that something has gone wrong. Credit accounts are those account which decreases when there are transactions. It is also known as var or als account which means always credit account because it always reduces when there are transactions relating to that accounts.
When using a manual accounting system, combination and special journals are great substitutes to the general journal as a convenient way of recording large numbers of similar transactions. However, despite the conveniences offered by these journals, using a computerized accounting system greatly enhances the efficiency of your entire accounting process. The column headings in a combination journal will depend on the needs of your business. Back in the day of manual accounting systems, the accounting department would manage countless journals and ledgers that contain all bookkeeping records.
They are used to record recurring, high-volume transactions that are of the same nature. If your business transactions are mostly cash-based, then all recordings can be made in the cash book rather than operating profit vs net income a combination journal. Any non-cash transactions are then recorded in the general journal. The number of accounts that you debited doesn’t have to be the same number of accounts that you credited.
- All other transactions not entered in a specialty journal account for in a General Journal.
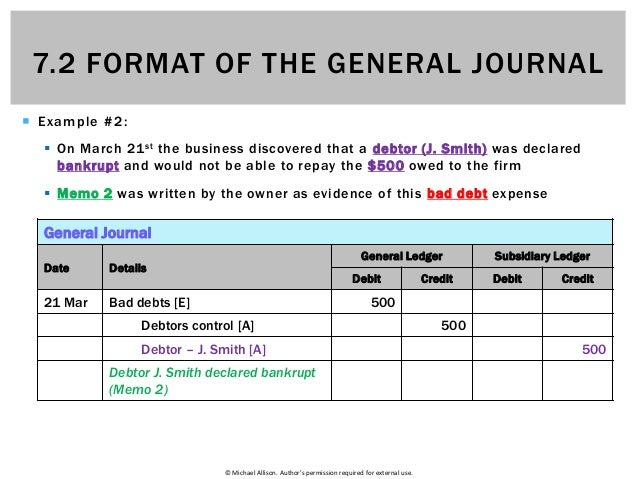
- It can have the transactions related to Accounts receivables, Accounts payable, Equipment, Accumulated depreciation, Expenses, Interest income and expenses, etc.
- Every entry contains an equal debit and credit along with the names of the accounts, description of the transaction, and date of the business event.
- No security deposit and advance rental payment was made by Mr. A to the lessor.
- These entries would then be totaled at the end of the period and transferred to the ledger.
It can help you understand how the data you recorded are captured and then processed into a set of financial statements. The Double-entry Bookkeeping is a system of recording transactions that involves recording at least two accounts that will result in a two-sided entry in the journal. This is the opposite of single-entry bookkeeping system which only involves one entry for each transaction. A general journal is the primary journal in which lower-volume accounting transactions are recorded, while the general ledger contains a summary of every recorded transaction.
All modern GLs are computerized with accounting software like Quickbooks, so GL maintenance is pretty simple. Now that we know what is in the GL, let’s take a look at how it is formatted. I also show you how to record the journal entry as well as explain the economic impact of each transaction on the accounting equation. Most of these journal entry examples are also in parts of the accounting course. If you don’t see what you are looking for, use the search bar on the right to find an example.
